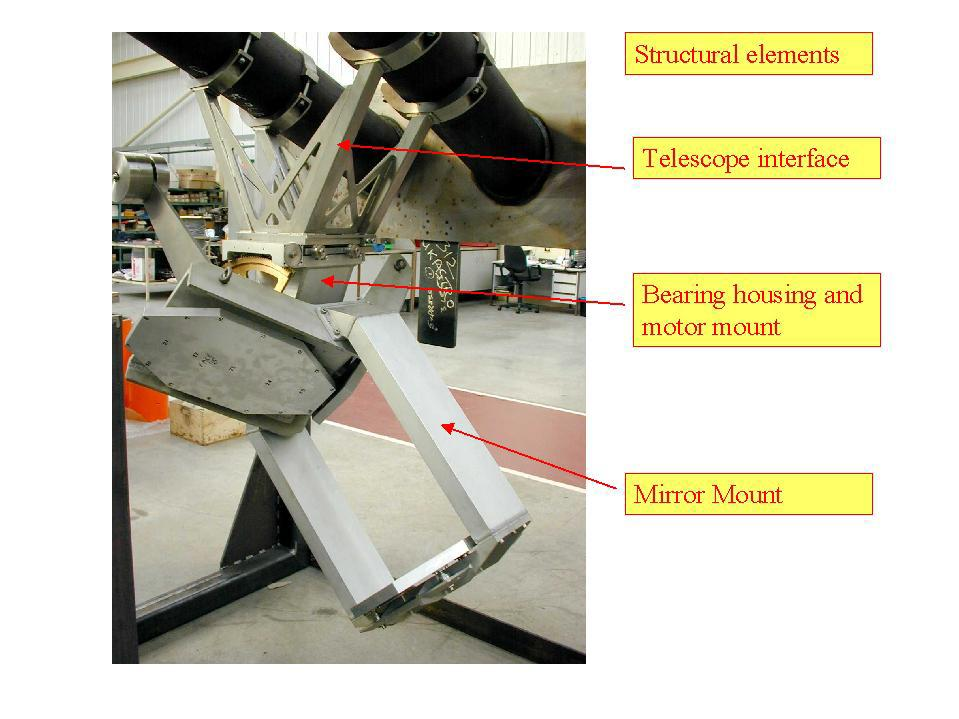
The K-mirror (adapted from Buckle, J.V., Hills, R.E., Smith, H., et al., 2009, MNRAS 399, 1026) consists of three large powered mirrors with modest curvature. The system acts as an image and polarization rotator and forms an image of the secondary mirror at a point near the elevation encoder. The figure shows the K-mirror on a test-mount. The K-mirror also maximizes the field of view available to the instrument on the Nasmyth platform (HARP), which otherwise would be severely limited due to the relatively small hole in the encoder axis. The K-mirror rotates as a unit about the elevation axis of the telescope and has a rotational range of ±57.5°, limited through control software to ±55°, with the effective rotation of the image and polarization twice the K-mirror rotation angle. The K-mirror can rotate at a rate of 5 deg/sec with a rotational position accuracy of ±0.1°. The design allows for a field of view of ∼200 arcsec. The system is designed to have very low losses and aberrations. Spillover loss is designed to be less than 1 per cent and, in fact, is expected to be <0.5 per cent at 850 μm. The losses per mirror should be less than 0.5 per cent at this wavelength, which will contribute ∼3 K to the system temperature from each mirror. In order to meet the needs of possible future JCMT instrumentation, the mirror surfaces have been finished so that they are compatible with the highest operational frequencies at the JCMT of ∼870 GHz.
Rotation of the K-mirror is controlled by the Telescope Control System (TCS). The TCS commands a continuous rotation of the K-mirror to compensate for the change in parallactic angle of the source and the rotation of the elevation axis of the telescope. In the coordinate frame specified by the observer (Ra/Dec, or Az/El) there will be four K-mirror position angles which result in an observation with the HARP array in the N-S/E-W direction: 0, 90, -180, -90 degrees (any observer-defined position angle in the MSB is added to these). Usually one of these angles is unreachable because of the ±55° rotation limits (which is ±110° on the sky) of the K-mirror.
When the telescope is commanded to slew to a new position, the TCS computes an optimal orientation of the focal plane relative to the tracking coordinate system to give the longest tracking time on source before hitting one of the K-mirror rotation limits. This optimal orientation corresponds to an initial K-mirror angle to which it is slewed, and then the TCS continuously updates the angle to maintain a fixed orientation between the focal plane and tracking coordinate systems throughout the observation.
In JCMTOT there is an option for HARP grid and jiggle observations to specify one or more desired K-mirror position angles, see here. If the angle(s) is/are not possible, the observation stops with an error. Preferably this option should be used in combination with a scheduling constraint for elevation (rising/setting) to prevent sending observations to the queue which are not possible.
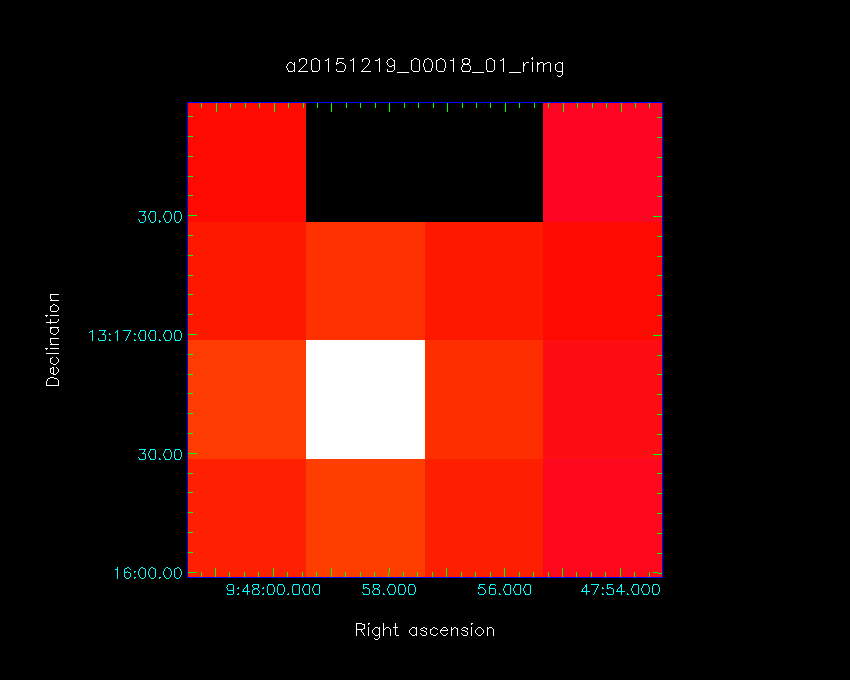
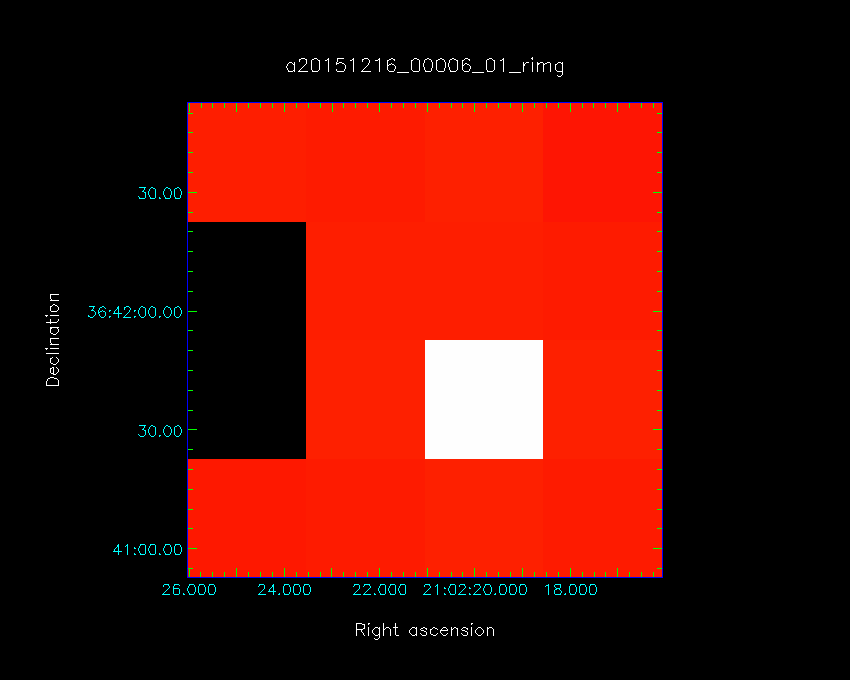
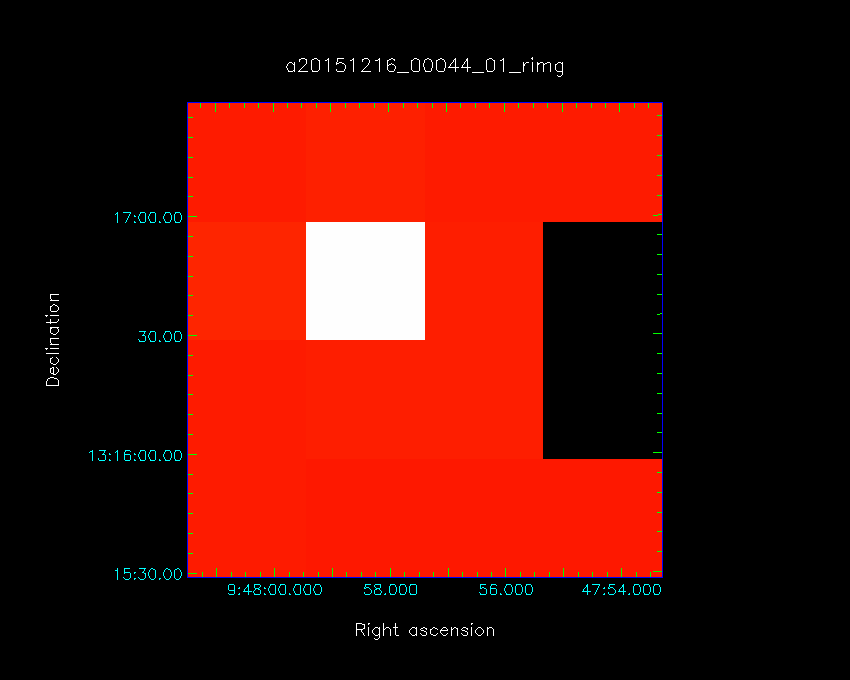
The orientation of the HARP array on the sky for the four K-mirror angles is shown in the figures below. The bright pixel is the tracking receptor H05, where the source is centered for pointing and pointed grid-observations.
The pointing offsets due to possible misalignment of the K-mirror axis and its axis of rotation have been calculated and included in the JCMT pointing model. The effective pointing of the telescope on the sky is changed if the mirrors are displaced or tilted. Residual rms pointing errors, after subtraction of the known correction terms, are typically about 2 arcseconds in Azimuth and Elevation. The K-mirror pointing model was much improved in April 2014.
The position of the K-mirror is recorded in the FITS-header variables ROT_PA and ROT_CRD, e.g.
ROT_PA = -0.4727979597822 / [deg] K-mirror angle
ROT_CRD = ‘TRACKING’ / K-mirror coordinate system